Importance of Breastmilk for Infants with Special Needs Breastmilk contains:
•Protective immune factors: Help to prevent infection
•Growth factors: Helps baby’s gut and other systems to develop as well as heal diarrhoea
•Enzymes: Make it easier to digest and absorb milk
•Special essential fatty acids help brain development
•Reduces pain from drawing blood or related to the baby’s condition,
•Gives the mother an important role in caring for her baby,
•Comforts the baby
•Strengthen bonding
Babies who require special attention are those who are:
•Not able to take oral feed
•Able to take oral feeds but not able to suckle
•Able to suckle but not for full feeds
•Not able to receive any breastmilk
 | ||
| COMPOSITION OF PRETERM HUMAN MILK (26 to 36 weeks POG) |
 | |||||||
| HEALTH ADVANTAGES OF HUMAN MILK FEEDING FOR PRETERM INFANTS |
How to Feed a Pre-Term Infant with Breastmilk?
For expressing breastmilk, you may start expressing after 6 hours post-delivery and collect in small amounts.
Baby can be fed using a syringe as well.
 |
| METHOD OF FEEDING PRE-TERM/ TERM LOW BIRTH WEIGHT BABIES |
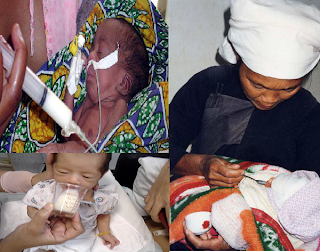 | |
| Clockwise from Top Left: IntraGastric Feeding, Spoon Feeding and Cup Feeding Methods |
Do ensure a LOTS and LOTS of SKIN TO SKIN Contact!!
SOME COMMON CONDITIONS :
(1) Breastmilk Jaundice
What is "Breastmilk Jaundice" ?
•Occurs in 5-10% of newborns
•Results from inadequate breastmilk volume or insufficient milk intake: Lead to dehydration, low caloric intake
•May occur in 1st week of life in breastfed infants
•Incidence may be reduced by:
–Encouraging early feeds
–Increasing frequency of feeds
–Avoiding use of water to replace breastmilk
Prevention of Severe Jaundice:
•Early initiation of breastfeeding
- Colostrum helps infants to pass the meconium, removes excess bilirubin from the body
•Encourage demand feeding: 8 – 12 feed a day
•Effective suckling: ensure effective milk tranfer
•No supplementary fluid
•Cup feeding with EBM if baby refuse to suck
(2) Babies with Cardiac Problems
•Babies may tire easily
•Short frequent feeds are helpful. The baby can breathe better when breastfeeding
•Breastfeeding is less stressful and less energy is used so there is better weight gain
•Breastmilk provides protection from illness thus reducing hospitalization and helping growth and development.
(3) Babies with Cleft Lip/Palate
•Babies with cleft lip only should be able to breastfeed - tissue of the breast can help the baby to create a seal more effectively
•Babies with a cleft palate are less likely to breastfeed directly from their mother's breast.
•Cleft palate babies often have problem with sucking, and may choke or gag on food that gets into their nose.(severe form )
•Cleft palate babies can be given EBM via special cleft palate bottle (Haberman feeder),spoon or cup.
•Encourage mom to put baby on breast for suckling and bonding
•Following surgery to repair the cleft, breastfeeding can resume as soon as the baby is alert.
Cleft lip and palate - How to feed?
•Hold the baby so that his or her nose and throat are higher than the breast
–This will prevent milk from leaking into the nasal cavity, which would make it difficult for the baby to breathe during the feed
•Breast tissue can fill a cleft in the lip to help the baby maintain suction.
(4) Babies with Down Syndrome
•Babies with Down Syndrome may have Hypotonia (weak Muscle Tone) and poor sucking reflex. Hence, this may lead to Poor Let Down which will result in Inadequate supply. To overcome this matter, Mummies are also encouraged to express milk and feed baby expressed breastmilk as well.
•Proper positioning,manual expression and supporting the breast so that infant do not lose nipple.
Hope this post is helpful for Mummies :-)
Source: National Lactation Centre
DISCLAIMER:
This post is just meant to be a stepping stone of awareness for mothers who have special need babies to not give up Breastfeeding without knowing that it is possible to proceed with breastfeeding.
However, kindly consult a paediatrician and lactation counsellour/consultant for proffesional advice because each individual case varies from one to another.










